The Indian automobile industry is one of the biggest industries in the world with a total amount of 26 crore vehicles (2015) and it is expected to cross 45 crore by 2020. Pollution conditions in India are going worse, so the Government of India has decided to make India a 100% EV nation by 2030. The demand for electric vehicles is increasing at a much faster rate than ever, it seems the future of electric vehicles in India is going to be superb.
When a vehicle does not move there is no electrical current supplied. A regulator is connected with the battery, which simply controls the amount of power received from the batteries so they don`t burn. The battery is used to power all electronic devices like in a car.
Since electric cars use an electric motor, the driver can take advantage of the motor's momentum when pressure is applied on the brakes. Instead of converting all the potential energy in the motor into heat as a fossil fuel car does, an electric car uses this forward momentum of the motor to recharge the battery. The whole process of recharging the battery while brakes are applied is called regenerative braking.
In short, the controller takes power from the battery and passes it to the electric motor. Before passing the current to a motor, the controller converts the Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC), 2 phase power which is suitable for a motor. The electric motor then converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical energy moves the vehicle forward and whenever brakes are applied it recharges the battery.
Here`s the process of how do electric cars charge.
Watch this whole video to fully understand how EV work.
Some brands will soon launch cheap hybrid cars in India.
Lets see how electric cars work animation.
For Better understanding about these types of EVs, watch this
Read this- Upcoming zero-emission cars in India
Also Read-
< Best Health and Wellness Technology in 2018
< Best Artificial Intelligence App for Android
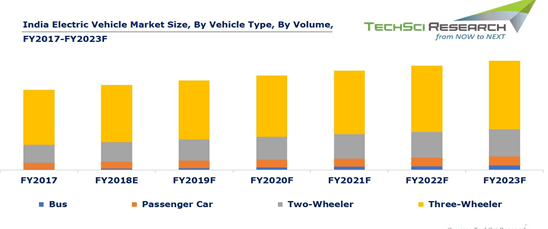
Future of electric vehicles in India
Let`s take a look at some of the features of EVs and what makes them so energy efficient. Take a look at some analysis.Highlights
- The Indian Government has decided to make India a 100% Electric Vehicle nation by 2030.
- Electric vehicles will very soon run at the cost of around 20 to 30 paise per km and can easily attain a top speed of 150km per hour.
- Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has decided to transfer its Ev battery technology to domestic EV manufacturers, due to this cost of EV will be cut up to 35%.
- In the near future, electric vehicles will have a mileage of 700-800 Km per charge.
- The government had launched the FAME India scheme way back in 2015 offering incentives on electric and hybrid electric vehicles of up to Rs 29,000 for bikes and Rs 1.38 lakh for cars.
Components of Electric Cars
Some of the electric cars components are shown in the figure. An electric vehicle has three primary components. These are the electric motor, motor controller, and battery.-
Battery
It is a powerhouse for the electric vehicle, it supplies electricity to motors. Aside from Li-ion battery technology, there are various other battery technologies which can be used for electric cars. For example Lead-acid batteries, Nickel batteries. -
Electric vehicle transmission
This system is used to deliver power, speed from a motor to wheels. Electric cars use an electric motor as the drive source at low speeds. In this case, no starting element is required because an electric motor can deliver sufficient torque at low rotational speeds. -
Electric Motor
An electrical motor is an electrical machine that converts electric energy into mechanical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, electrical generators or inverters.
Also Read- Electric Vehicles
Electric car working principle
The Electric vehicles get power from the rechargeable batteries installed inside the car. These batteries are not only used to power vehicles but also used for other functioning. From outside every electric car looks the same as conventional fossil fuel car, but in place of a fuel tank, there is a battery which acts as a power source.When a vehicle does not move there is no electrical current supplied. A regulator is connected with the battery, which simply controls the amount of power received from the batteries so they don`t burn. The battery is used to power all electronic devices like in a car.
Since electric cars use an electric motor, the driver can take advantage of the motor's momentum when pressure is applied on the brakes. Instead of converting all the potential energy in the motor into heat as a fossil fuel car does, an electric car uses this forward momentum of the motor to recharge the battery. The whole process of recharging the battery while brakes are applied is called regenerative braking.
In short, the controller takes power from the battery and passes it to the electric motor. Before passing the current to a motor, the controller converts the Direct Current (DC) into Alternating Current (AC), 2 phase power which is suitable for a motor. The electric motor then converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. The mechanical energy moves the vehicle forward and whenever brakes are applied it recharges the battery.
Here`s the process of how do electric cars charge.
Watch this whole video to fully understand how EV work.
Types of electric vehicles
There are three main types of electric vehicles (EVs) which are available in the market.Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs)
These vehicles are 100% electric, also known as “100% electric” or “pure electric vehicles”, are wholly driven by an electric motor, powered by a battery that can be plugged into the mains. There is no combustion engine, fuel tank, and exhaust pipe. Pure electric vehicles are also known as ‘plug-in’ EVs as they use an external electrical charging outlet to charge the battery. When the vehicle is slowing down, the motor is put into reverse to slow down the vehicle, acting as a small-generator to top-up the battery. The process is known as Regenerative braking and this extra feature can add 10 miles or more to the range of the vehicle. Models like BMW i3 and the Nissan Leaf which produces zero CO2 exhaust emissions are an example of BEVs.Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs)
The battery in PHEVs is much smaller than in a 100% electric vehicle and tends to drive the wheels at low speeds or for a limited range. After the battery is fully drained, the hybrid capability means that the vehicle can continue journeys powered by its conventional fossil fuel engine. The use of an IC engine that is plugged-in hybrid vehicles tends to have tailpipe emissions of around 40-75g/km CO2 when measured against the current European test cycle. PHEVs models are Toyota Prius, Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV.Extended-Range Electric Vehicles (E-REV)
EREVs have a plug-in battery, electric motor, as well as an internal combustion engine. The main difference between PHEVs and EREVs are that the electric motor always drives the wheels with the IC engine acting as a generator to recharge the battery when it is depleted. EREVs can have a pure electric range of up to 125 miles. This results in tailpipe emissions of less than 20g/km CO2. Example- Honda Civic Hybrid.Some brands will soon launch cheap hybrid cars in India.
Lets see how electric cars work animation.
For Better understanding about these types of EVs, watch this
EV Price in India
Take a look at electric cars in India price list.Read this- Upcoming zero-emission cars in India
Conclusion:
We hope you have got all the needed information from our post "future of electric vehicles in India". Let us know in the comment section and if you think it was helpful then Share it with your friends, family, everywhere. Thank you for reading this post.Also Read-
< Best Health and Wellness Technology in 2018
< Best Artificial Intelligence App for Android






1 Comments
Happy New Year Friends
ReplyDelete